119 lines
5.1 KiB
Markdown
119 lines
5.1 KiB
Markdown
# GeoStat
|
|
### Version 2.0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GeoStat it's a Python-based script for parsing Nginx and Apache log files and getting GEO data from incoming IPs from it. This script converts parsed data into JSON format and sends it to the InfluxDB database, so you can use it for building nice Grafana dashboards for example. The application runs as SystemD service and parses log files in "tailf" style. Also, you can run it as a Docker container if you wish.
|
|
|
|
# New in version 2.0
|
|
- The application was rewritten with python3
|
|
- Was added few additional tags to JSON output, the country name, and the city name.
|
|
- Was fixed the few bugs with the geohash lib and with the install.sh script.
|
|
- Also was added the simple logging feature, now you can catch this application log in the Syslog file.
|
|
- The Dockerfile was recreated with the python3 support also.
|
|
- Was done all needed tests, and all things looks OK :)
|
|
|
|
# Main Features:
|
|
|
|
- Parsing incoming IPs from web server log and converts them into GEO metrics for the InfluxDB.
|
|
- Using standard python libs for maximum easy use.
|
|
- Having an external **settings.ini** file for comfortable changing parameters.
|
|
- Having a Dockerfile inside for quick building Docker image.
|
|
- Contains an install.sh script that will do the installation process easy.
|
|
- Runs as a SystemD service
|
|
|
|
JSON format that script sends to InfluxDB looks like:
|
|
```
|
|
[
|
|
{
|
|
'fields': {
|
|
'count': 1
|
|
},
|
|
'measurement': 'geo_cube',
|
|
'tags': {
|
|
'host': 'cube'
|
|
'geohash': 'u8mb76rpv69r',
|
|
'country_code': 'UA'
|
|
'country_name': 'Ukraine'
|
|
'city_name': 'Odessa'
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
]
|
|
```
|
|
As you can see there are five fields in the JSON output, so you can build dashboards using geo-hash (with a point on the map) or country code, or with the country name and city name. Build dashboards with variables based on the hostname tag or combine them all. A count for any metric equals 1, so it'll be easy summarising. This script doesn't parse the log file from the beginning but parses it line by line after starting. So you can build dashboards using **count** of data after some time will pass.
|
|
|
|
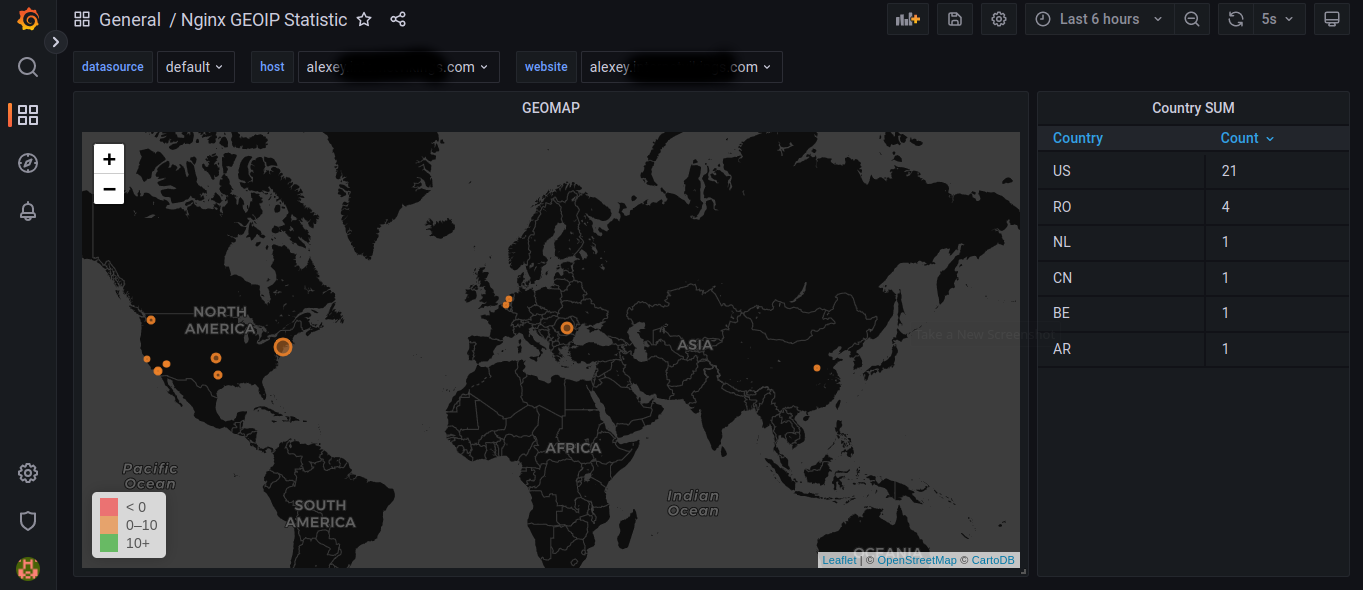
You can find the example of the Grafana dashboard in **geomap.json** file or take it from the grafana.com: https://grafana.com/dashboards/8342
|
|
|
|
### Tech
|
|
|
|
GeoStat uses a number of open source libs to work properly:
|
|
|
|
* [Geohash](https://github.com/vinsci/geohash) - Python module that provides functions for decoding and encoding Geohashes. Now it was added as local lib, and no longer need to be installed with pip.
|
|
* [InfluxDB-Python](https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb-python) - Python client for InfluxDB.
|
|
|
|
## Important
|
|
The GeoLite2-City database no longer available for the simple downloading, now you need register on the maxmind.com website first.
|
|
After you'll get an account on the maxmind.com you can find the needed file by the link
|
|
|
|
(https://www.maxmind.com/en/accounts/YOURACCOUNTID/geoip/downloads)
|
|
|
|
Please don't forget to unzip and put the GeoLite2-City.mmdb file in the same directory with the geoparse.py script, or you can put it anywhere and then fix the path in the settings.ini.
|
|
|
|
# Installation
|
|
|
|
You can install it in a few ways:
|
|
|
|
Using install.sh script:
|
|
1) Clone the repository.
|
|
2) CD into the directory and then run **install.sh**, it will asks you to set properly settings.ini parameters, like Nginx/Apache **access.log** path, and InfluxDB settings.
|
|
3) After the script will finish the application installationion you need copy the GeoLite2-City.mmdb file into the application local directory and start the SystemD service with **systemctl start geostat.service**.
|
|
|
|
Manually:
|
|
1) Clone the repository, create an environment and install requirements
|
|
```sh
|
|
$ cd geostat
|
|
$ python3 -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate
|
|
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
|
|
```
|
|
2) Modify **settings.ini** & **geostat.service** files and copy service to systemd.
|
|
```sh
|
|
$ cp settings.ini.bak settings.ini
|
|
$ vi settings.ini
|
|
$ cp geostat.service.template geostat.service
|
|
$ vi geostat.service
|
|
$ cp geostat.service /lib/systemd/system/
|
|
```
|
|
3) Register and download latest GeoLite2-City.mmdb file from maxmind.com
|
|
```sh
|
|
$ cp ./any_path/GeoLite2-City.mmdb ./
|
|
```
|
|
4) Then enable and start service
|
|
```sh
|
|
$ systemctl enable geostat.service
|
|
$ systemctl start geostat.service
|
|
```
|
|
Using Docker image:
|
|
1) Build the docker image using the Dockerfile inside geostat repository directory:
|
|
```
|
|
$ docker build -t some-name/geostat .
|
|
```
|
|
2) Register and download latest GeoLite2-City.mmdb file from maxmind.com
|
|
```sh
|
|
$ cp ./any_path/GeoLite2-City.mmdb ./
|
|
```
|
|
3) After Docker image will be created you can run it using properly edited **settings.ini** file and you also,
|
|
need to forward the Nginx/Apache logfile inside the container:
|
|
```
|
|
docker run -d --name geostat -v /opt/geostat/settings.ini:/settings.ini -v /var/log/nginx_access.log:/var/log/nginx_access.log some-name/geostat
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
After the first metrics will reach the InfluxDB you can create nice dashboards in Grafana.
|
|
|
|
Have fun !
|
|
|
|
License
|
|
----
|
|
|
|
MIT
|
|
|
|
**Free Software, Hell Yeah!**
|